DIY Redis
By: Sid
Here's all you need to know to build your own redis server.
Built this at as a in-house cache at work, used go lang for multiple benefits but essentially cause my project was based off of go-lang :P
RDB's
Persistence is a key when you're building something like Redis. Read up on how Redis handles persistence here : They technically have 4 ways of handling persistence :
1.RDB files
2.AOF
3.No Persistence => not very smart eh ?
4.RDB + AOF
For my implementation, I chose to use RDB files and here's how I did it :
What is an RDB file?
It's basically a binary snapshot of your redis data at a given time-frame.
What does an RDB file contain? (this is basically the map in the code)
- A header identifying it as Redis data, plus the version number.
- Auxiliary fields (metadata like the Redis server version).
- One or more “database sections”, each corresponding to a numbered Redis database (0, 1, 2, …).
- Within each section, a list of key/value pairs—and for keys with expirations, a timestamp.
- A final end-of-file marker to signal “that’s all folks.”
Ok, I think it get's easier if you consider this example :
Imagine your dump.rdb is like this :
1.Header: REDIS0008 (version 8)
2.AUX: redis_version → 6.2.5
3.DB 0: two keys
foo = bar (no expiry)
baz = quxqu (expires at timestamp 2018)
4.EOF marker
When you run the parser:
1.Header check - Reads REDIS0008 → sets version = 8.
2.AUX loop - Sees 0xFA, reads “redis_version” / “6.2.5” → stores in metadata.
3.DB loop - Sees 0xFE, reads DB index 0. - Reads “2 keys total” and “1 has TTL.”
4.Entry loop -
4.1. First entry: no 0xFC, so reads key “foo” and value “bar” → puts it in KeyValues.
4.2. Second entry: finds 0xFC, reads expiry 2018 → then reads key “baz” and value “quxqu” → puts it in TTLRecords. 5. EOF - Reads 0xFF → stops parsing.
at the end, this is how the map should look like
DumpParser{
version: 8,
metadata: map[string]string{"redis_version": "6.2.5"},
Databases: []DatabaseSection{
{
ID: 0,
TotalEntries: 2,
TTL: 1,
KeyValues: map[string]string{"foo": "bar"},
TTLRecords: []TTLRecord{{Key: "baz", Value: "quxqu", ExpireAt: 2018}},
},
},
}
as you can see, KeyValues & TTLRecords(for expiry) will technically have the data stored into and how I've programmed the parser is :
1.if you see the byte 0xFA, read two strings (key and value) and stash them in metadata. => essentially, the AUX Loop mentioned above
2.you see 0xFE, read the database number, then the counts (total keys, how many of them have TTLs). => essentially, the DB Loop mentioned above
Now, lets look at how we'll parse RESP, but first, lets look up what RESP is :
What’s RESP, anyway?
This is the second thing you need to know when building your Redis! RESP (REdis Serialization Protocol) is the simple text-based wire format Redis uses to talk to clients. Read up more on RESP here!
Arrays start with: \*<count>\r\n
Bulk strings start with: $<length>\r\n<string bytes>\r\n
Integers start with: :<number>\r\n
Simple strings start with: +<text>\r\n
Errors start with: -<message>\r\n
Again, let's consider another example of SET foo bar
this command effectively sets the value bar to the key foo
The SET foo bar command is sent as follows :
*3\r\n ← Array of 3 elements
$3\r\nSET\r\n ← Bulk string “SET”
$3\r\nfoo\r\n ← Bulk string “foo”
$3\r\nbar\r\n ← Bulk string “bar”
Here's how I desgined my RESP parser :
- Peeks at the first byte to see which RESP type it is
(\*, $, :, or otherwise). - Dispatches to the right sub-parser:
2.1ParseArray()
2.2ParseBulk()
2.3integer parser
2.4simple string fallback
Key helpers
readLine()reads up to\r\nand trims itreadLength()usesreadLine()thenstrconv.Atoito parse the count or lengthParseBulk()reads the length, then exactly that many bytes plus the trailing\r\n
We also have to create the encode commands when sending messages, so the respective functions have to be made as well !
Putting all this together with a single file to parse the command line arguments and requests is the final step after making the RBD parser and the RESP parser.
Once you do that, you should have a perfect REDIS server that works with REDIS client
Here's a couple of things my server can handle as of now
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
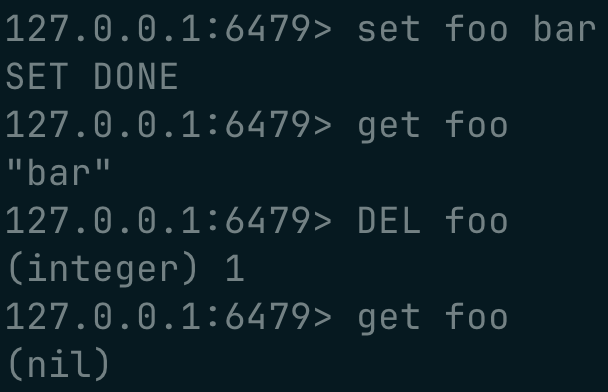
SET key value | Set a key to a value |
GET key | Get the value of a key |
DEL key | Delete a key |
PX key seconds | Set TTL for a key |
INCR key | Increment a key’s integer value |
MULTI / EXEC | Start and execute a transaction |
PING | Ping the server |
and here are a couple of example screenshots !
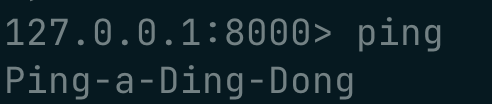 working with strings :
working with strings :
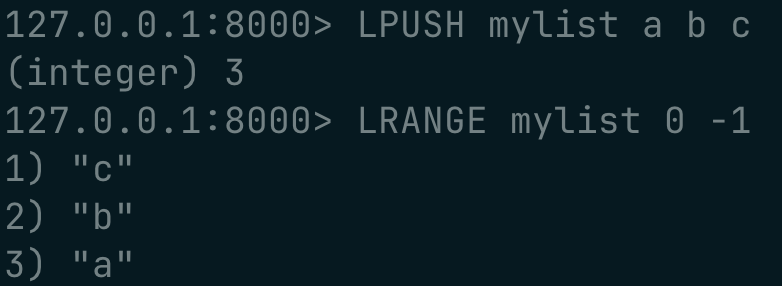
 working with lists :
working with lists :
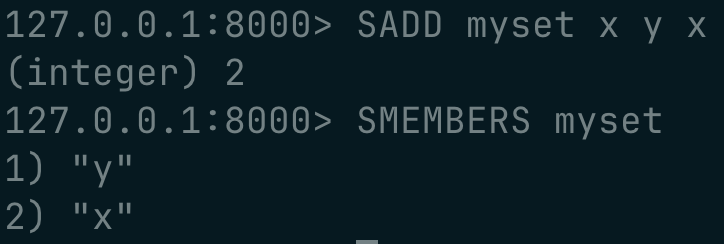
 working with sets :
working with sets :
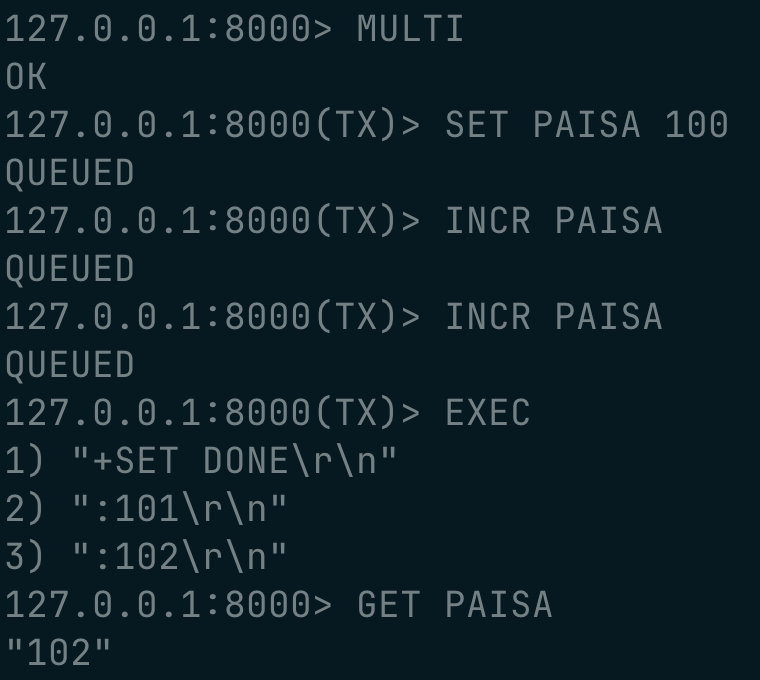
 using transactions :
using transactions :
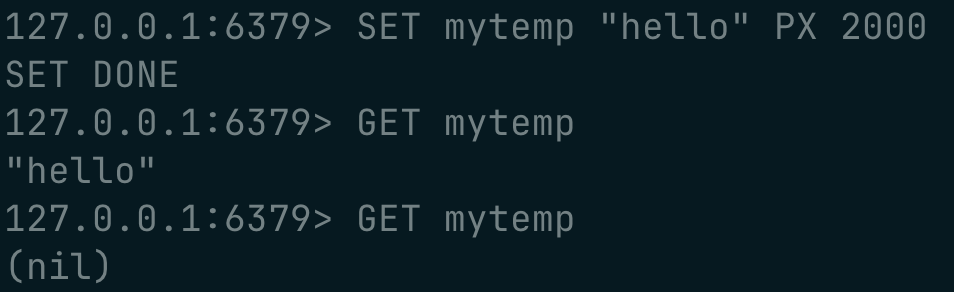
 using expiration on values :
using expiration on values :
In the coming week's I plan on adding the following :
- supporting more data types, rn supports strings, lists and sets.
- snapshotting of rdb and AOF.
thanks for tuning in !